Eye is one of the most commonly affected organs in people with diabetes. Eye complications can be relatively harmless, while can lead to blindness in its most difficult form! Diabetes is the leading cause of low vision and blindness among the working-age population in Europe, which causes enormous treatment costs and disability due to inability to work.
Diabetes is one of the main causes of blindness, kidney failure, heart attack, and stroke, so it's no wonder it’s called a "silent killer." The number of people with diabetes increased from 108 million in 1980 to as many as 422 million in 2014. The cause of the increase in newly ill is, among other things, hidden in the intake of high-calorie food and reduced physical activity. In Croatia, about 255,000 people with diabetes are currently registered, with about 40% of people still not diagnosed.
Diabetes is a chronic, and unfortunately, still an incurable disease that attacks the entire body. This is primarily vasculopathy, i.e. blood vessel disease. Since our organism requires continuous blood flow to all cells, there is no organ s in our body that remains spared from this disease.
An eye is one of the most commonly affected organs in people with diabetes. Eye complications can be relatively harmless, while in its most difficult form can lead to blindness! Diabetes is the leading cause of low vision and blindness among the working-age population in Europe, which causes enormous treatment costs and disability due to inability to work. Diabetes can damage the whole eye, and diabetics themselves more often complain about dry eye symptoms such as tingling, tearing or feeling of eye irritation.
It is believed that diabetes accelerates the development of cataract that leads to visual impairment, and it’s up to three times more common with people of the same age who are not diabetic.
The most important and most dangerous complication of diabetes on the eye is diabetic retinopathy. It’s a condition when diabetes damages the blood vessels in the back of the eye called the retina. The retina is an inner layer of the eye, very thin, consisting exclusively of nerve fibres. It is believed that about 90% of people with diabetes have some degree of retinal damage.
For people with diabetic retinopathy, due to damage to blood vessels in the centre of the eye, i.e. macula or yellow spot, a fluid build-up occurs in the nerves. This condition is called diabetic macular oedema and always leads to central vision impairment. A person perceives it as a straight-line distortion, inability to read or recognition of the details on the face. If this condition is not treated, it causes permanent nerve damage and permanent vision loss.
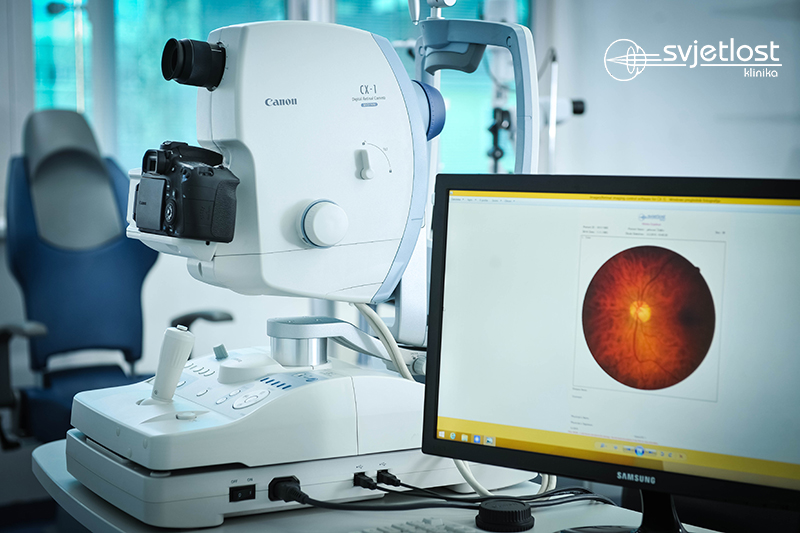
The disease is easily diagnosed and followed by modern diagnostic methods such as OCT or optical coherent tomography. It is a fast and completely secure method that gives the exact view of eye centre, i.e. yellow spot. OCT, especially the use of injections directly into the eye, led to a revolution in the treatment of this severe of diabetes ocular complication.
Many types of medication are developed today. They are completely safe, fast and painlessly injected in the eye and enable not only certain vision loss prevention but also getting vision closer to a former condition in most of the patients.
In addition to diabetic eye damage, i.e. diabetic macular oedema, diabetes in the eye, due to poor circulation, also leads to the growth of wild blood vessels i.e. neovascularization. These newly developed blood vessels often sprain, causing bleeding in the inside of the eye. One perceives it as a sudden weakening of the vision. In addition to these newly formed blood vessels, connective tissue is also growing. Connective tissue can, however, lead to retinal detachment or ablation. This is considered the most severe complication of diabetes in the eye.
The laser is traditionally being used to counteract the growth of these wild blood vessels and connective tissue. If the disease is in an advanced stage, the surgery is necessary.
For eye cleansing and retinal detachment repair, an operation called vitrectomy is performed. This operation is performed routinely, in local anaesthesia and is painless. From all that, the treatment of diabetes complications on the eye has become very successful and safe nowadays. But we all want this complication not to come. Therefore, prevention that is achieved by regular eye exams and good sugar control is paramount!
After diagnosing diabetes, an ocular background should be examined immediately. This is immensely important because most patients at the time of diagnosing diabetes have no eye damage. It is considered that at least 5 years of diabetes are required to cause eye damage. However, if a diabetic understands the importance of changing lifestyle, diet, regular medication and team collaboration with doctors, eye damage doesn’t have to occur at all or will be in the initial stage and won’t even have to be treated.
With such responsible behaviour, quality of life is preserved in the long term and the cost of the health system is minimized. The team of ophthalmologist at Svjetlost Clinic will help you with a little of your own engagement to preserve the vision as well as the quality of your life!
Dr. Mirko Ratković, Ophthalmologist, Retinal Department
Diabetes is a chronic, and unfortunately, still an incurable disease that attacks the entire body. This is primarily vasculopathy, i.e. blood vessel disease. Since our organism requires continuous blood flow to all cells, there is no organ s in our body that remains spared from this disease.
An eye is one of the most commonly affected organs in people with diabetes. Eye complications can be relatively harmless, while in its most difficult form can lead to blindness! Diabetes is the leading cause of low vision and blindness among the working-age population in Europe, which causes enormous treatment costs and disability due to inability to work. Diabetes can damage the whole eye, and diabetics themselves more often complain about dry eye symptoms such as tingling, tearing or feeling of eye irritation.
It is believed that diabetes accelerates the development of cataract that leads to visual impairment, and it’s up to three times more common with people of the same age who are not diabetic.
The most important and most dangerous complication of diabetes on the eye is diabetic retinopathy. It’s a condition when diabetes damages the blood vessels in the back of the eye called the retina. The retina is an inner layer of the eye, very thin, consisting exclusively of nerve fibres. It is believed that about 90% of people with diabetes have some degree of retinal damage.
For people with diabetic retinopathy, due to damage to blood vessels in the centre of the eye, i.e. macula or yellow spot, a fluid build-up occurs in the nerves. This condition is called diabetic macular oedema and always leads to central vision impairment. A person perceives it as a straight-line distortion, inability to read or recognition of the details on the face. If this condition is not treated, it causes permanent nerve damage and permanent vision loss.
The disease is easily diagnosed and followed by modern diagnostic methods such as OCT or optical coherent tomography. It is a fast and completely secure method that gives the exact view of eye centre, i.e. yellow spot. OCT, especially the use of injections directly into the eye, led to a revolution in the treatment of this severe of diabetes ocular complication.
Many types of medication are developed today. They are completely safe, fast and painlessly injected in the eye and enable not only certain vision loss prevention but also getting vision closer to a former condition in most of the patients.
In addition to diabetic eye damage, i.e. diabetic macular oedema, diabetes in the eye, due to poor circulation, also leads to the growth of wild blood vessels i.e. neovascularization. These newly developed blood vessels often sprain, causing bleeding in the inside of the eye. One perceives it as a sudden weakening of the vision. In addition to these newly formed blood vessels, connective tissue is also growing. Connective tissue can, however, lead to retinal detachment or ablation. This is considered the most severe complication of diabetes in the eye.
The laser is traditionally being used to counteract the growth of these wild blood vessels and connective tissue. If the disease is in an advanced stage, the surgery is necessary.
For eye cleansing and retinal detachment repair, an operation called vitrectomy is performed. This operation is performed routinely, in local anaesthesia and is painless. From all that, the treatment of diabetes complications on the eye has become very successful and safe nowadays. But we all want this complication not to come. Therefore, prevention that is achieved by regular eye exams and good sugar control is paramount!
After diagnosing diabetes, an ocular background should be examined immediately. This is immensely important because most patients at the time of diagnosing diabetes have no eye damage. It is considered that at least 5 years of diabetes are required to cause eye damage. However, if a diabetic understands the importance of changing lifestyle, diet, regular medication and team collaboration with doctors, eye damage doesn’t have to occur at all or will be in the initial stage and won’t even have to be treated.
With such responsible behaviour, quality of life is preserved in the long term and the cost of the health system is minimized. The team of ophthalmologist at Svjetlost Clinic will help you with a little of your own engagement to preserve the vision as well as the quality of your life!
Dr. Mirko Ratković, Ophthalmologist, Retinal Department