What to expect during examination of vitreous and retina?
The examination of the deeper part of the eye begins by determining visual acuity in both eyes. Next is the measurement of intraocular pressure and examination on a slit-lamp to determine whether there is transparency of the cornea or cataract present.
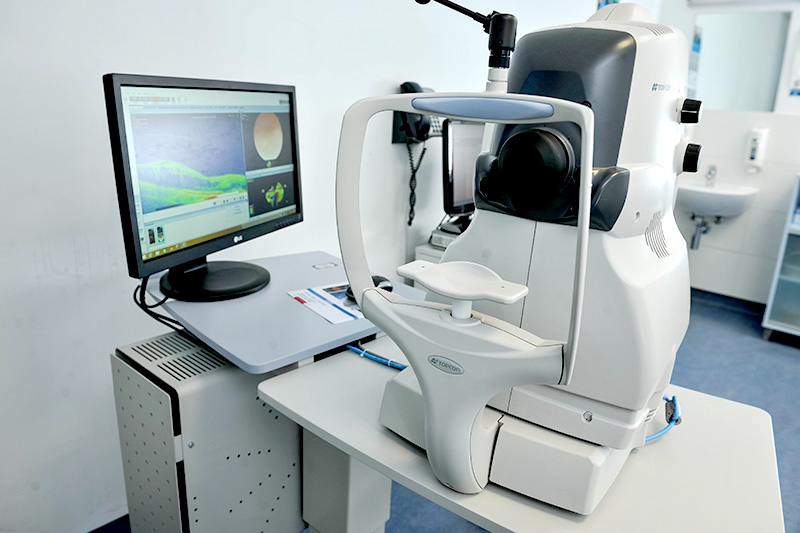
The pupils remain dilated after examination for 2 hours so it is difficult to read and drive a car after the examination for a period of 2 hours. On average, it takes around 10 minutes up to half an hour to dilate the pupils depending on individual patient. The examination of the deeper part of the eye is performed in office on slit-lamp. An eye doctor positions a magnifying lens near the eye or on the anaesthetized eye. In this way we can see the details of the fundus: vitreous and retina. The examination lasts 1 hour and it's painless. After the examination, the patient can see a glare for few minutes.
What happens after the examination?
After the examination, a doctor can make a diagnosis and decide on treatment or order additional tests. Usually, the examination is followed by additional tests such as: OCT-optical coherence tomography, fluorescein angiography or ultrasound of the eye. All of these tests can be done immediately and no new appoinments are needed.
After additional tests, the doctor decides on treatment (eye drops, laser, intraocular injections) or surgery is scheduled. All these treatments can be performed immediately on the same day. If surgery is urgent, it can be organized on the same day, for example in the case of retinal detachment or eye injury caused by a foreign body.
Will a check-up be required?
Retinal diseases are often complex diseases with chronic course.Therefore it is usually necessary to monitor patients for a long time at weekly or monthly intervals. At the check-ups, the pupils are also dilated, and certain tests can be performed, but the check-up is usually shorter then initial examination.

 The pupils remain dilated after examination for 2 hours so it is difficult to read and drive a car after the examination for a period of 2 hours. On average, it takes around 10 minutes up to half an hour to dilate the pupils depending on individual patient. The examination of the deeper part of the eye is performed in office on slit-lamp. An eye doctor positions a magnifying lens near the eye or on the anaesthetized eye. In this way we can see the details of the fundus: vitreous and retina. The examination lasts 1 hour and it's painless. After the examination, the patient can see a glare for few minutes.
The pupils remain dilated after examination for 2 hours so it is difficult to read and drive a car after the examination for a period of 2 hours. On average, it takes around 10 minutes up to half an hour to dilate the pupils depending on individual patient. The examination of the deeper part of the eye is performed in office on slit-lamp. An eye doctor positions a magnifying lens near the eye or on the anaesthetized eye. In this way we can see the details of the fundus: vitreous and retina. The examination lasts 1 hour and it's painless. After the examination, the patient can see a glare for few minutes.
