How is the surgery done?
Depending on corneal disease and whether the pathological process affected the full thickness of the cornea or only its surface, it is possible to adjust the surgical technique and apply the perforating keratoplasty (full thickness corneal transplantation) or lamellar corneal transplantation (partial thickness transplantation depending on which part is affected by the diseas) .
Under which anesthesia is the surgery performed?
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia orunder local anesthesia potentiated by intravenous sedation. The procedure of corneal transplantation lasts on average 30 min.
How often must the patient be controlled after the surgery?
The first 7-10 days everyday controls are necessary. After that, the controls are weekly, then every other week, and than monthly throughout first 6 months. After 6 months, controls are done on 2-3 months basis up to one postoperative year, and even less often when the situation is stable.
Penetrating corneal transplantation
What is penetrating transplantation?
Penetrating transplantation is an operation in which a full thickness of the sick cornea is replaced with a healthy donor cornea. Recovery of eyesight is much slower compared to the lamellar transplantation, but today it is still used for diseases that affect all layers of the cornea.
This method of transplantation has been the gold standard in the treatment of corneal diseases for more than a century and is still indispensable in cases of scars (leucoma) affecting the full thickness of the cornea, corneal hydrops, preperforations of the cornea and perforating corneal injuries.
How is the transplant placefixed into?
The transplant is fixed by very thin sutures that can be (but need not be) taken off after about a year. The surgery is performed under general or local anesthesia and lasts an average of 30 minutes. The first 7-10 days everyday controls are necessary.
How does the recovery after the surgery function?
Already at few days after the surgery, the patient achieves better eyesight than he had before, but to reach the full recovery of the eyesight with this method of corneal transplants, one should wait for a few months.
Lamellar corneal transplantation (e.g. DSAEK, UT-DSAEK)
What is lamellar transplantation?
Lamellar transplantation (DSAEK, UT-DSAEK) is advanced technique in which only the diseased portion of the cornea is transplanted.
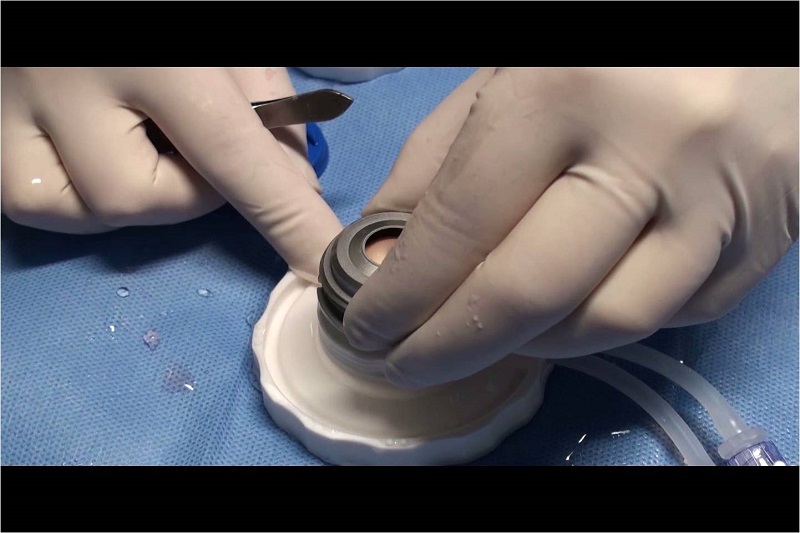
How does the recovery of eyesight after the surgery function?
The eyesight recovers quickly, already within a few weeks; the possibility of complications is small and rejection of the transplanted corneal is extremely rare.
For how long have these operations been performed?
They have been performed in the world during the last ten years and in the Clinic Svjetlost for the last six years. Head of Cornea department, prof. Iva Dekaris performed first DSAEK and UT-DSAEK operation in Croatia, which are also among the first ones in Europe, and she has been invited speaker on this topic at the most eminent European Congresses of Ophthalmology. She is the author of the chapter on UT-DSAEK corneal transplantation in the European textbook issued in 2015.
DSAEK (Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty)
DSAEK is posterior lamellar transplantation which is used in cases where the front of the cornea is clear, and the disease affects only corneal endothelium (inner layer of the cornea).
By which corneal diseases is this method of transplantation performed?
This method of lamellar transplantation is applied for diseases such as: pseudophakic bullous keratopathy, Fuchs' dystrophy, decompensated previous corneal graft etc. DSAEK is the most commonly performed corneal transplantation method in America and accounts for 60% of all corneal grafts in USA.
What is the advantage of this type of transplantation?
The advantage is that the biggest hole on the surface of the eye is only 3 mm and such a small incision preserves the normal curvature of the cornea which is important for better eyesight and integrity of the globe. Postoperative recovery is fast and good vision is achieved in just a few weeks. After the perforating keratoplasty, several months are needed for the recovery of visual acuity.
What type of anesthesia is used in lamellar transplantation?
Lamellar transplantion is usually performed under anesthesia with intravenous sedation.
Are there fewer complications?
Intraoperative complications occur less often then with penetrating transplantation. The complications associated with sutures meaning neovascularization and possibility of infection is significantly reduced by this method. Unlike penetrating keratoplasty, only three sutures are placed on the incision and can be taken off already in the second post-operative month. Transplant rejection reactions are ten times less often in comparison with the perforating transplantation.
What else affects the recovery of eyesight?
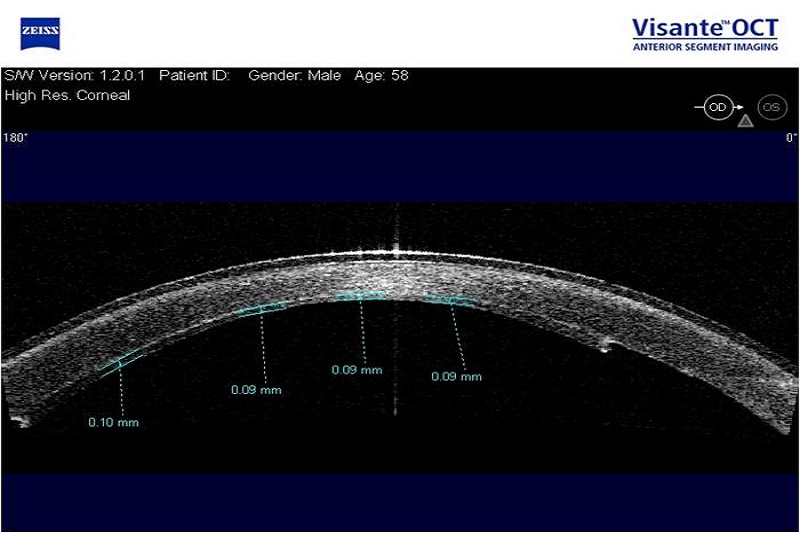
In achieving better eyesight after DSAEK, a major role has the time period of the disease in case of pseudophakic bullous keratopathy (the earlier the operation is done, counting from the onset of the disease, the better the eyesight is!) and thickness of the endothelial transplant (the thinner the better!). Therefore, in recent years, the technique of endothelial UT-DSAEK transplantation has been developed in which the donor tissue layer is extremely thin.
UT-DSAEK (Ultra Thin Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty)
UT-DSAEK is also the method of posterior lamellar keratoplasty designed by Italian ophthalmologist Prof. Busin.
What is the difference between DSAEK and UT-DSAEK?
The difference from conventional DSAEK is in the preparation of endothelial transplants so that a very thin donor tissue of not more then 100 microns is obtained.
What is the visual acuity after UT-DSAEK?
Visual acuity after UT-DSAEK is often 100% and is achieved in a shorter period of time than after penetrating transplantation or DSAEK. The eyesight after this procedure is entirely comparable with DMEK technique (a technique in which only the membrane that carries the endothelium and endothelial cells is transplanted). The advantage over the DMEK is that the UT-DSAEK transplant is significantly less often "detached" from the recipient cornea compared to DMEK transplant and therefore this is the method of choice for endothelial transplantation in our Clinic.


